Date: 29 Jul 2024
1. What is the main function of roots
The main function of roots is to anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and nutrients from it. The roots also provide support to the plant, helping it to remain upright and stable. In addition to these basic functions, roots can perform a number of other important tasks. For example, some roots are specialized for storing nutrients, such as carbohydrates, that the plant can use for energy during times of stress or dormancy. Other roots are adapted for reproductive purposes, such as the production of seeds or spores. In general, the root system plays a vital role in the health and growth of the plant.
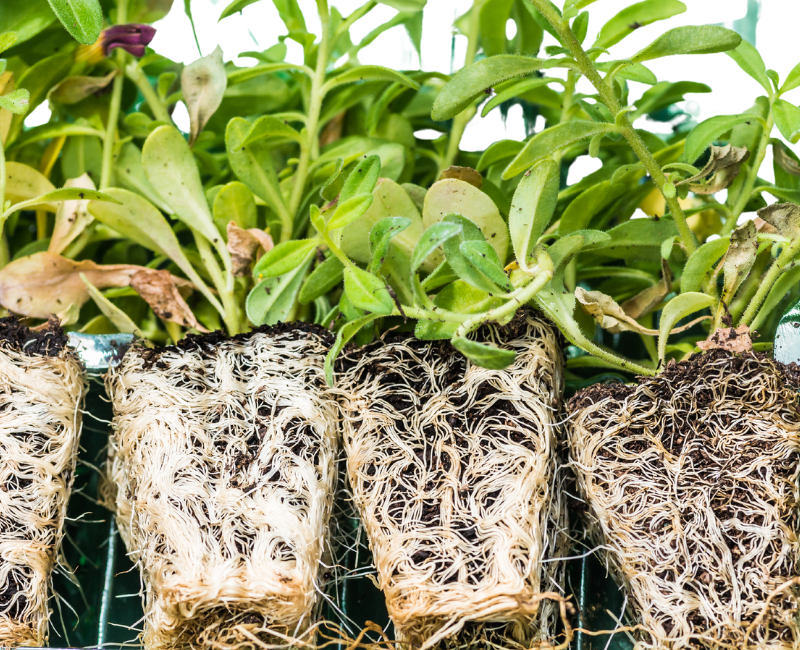

2. How roots are formed
Plant roots are formed by cells in the root meristem, which is a small group of actively dividing cells located near the tip of the root. As the plant grows, the cells in the root meristem differentiate into different types of root tissue, such as root hairs, vascular tissue, and cortex. The arrangement of these tissues helps the root absorb water and nutrients from the soil and transport them to other parts of the plant.
Root growth begins when the seed germinates and a small root called a radicle emerges from the seed. As the radicle grows, it begins to produce lateral roots that branch off from the main root and grow in different directions. A plant's root system can continue to grow and develop throughout the life of the plant, adapting to the availability of resources in the soil and the changing needs of the plant.
3. How long do roots grow?
The roots will continue to grow as long as the plant is alive and healthy. In some plants, the root system can continue to develop and expand throughout the life of the plant, adapting to the available resources in the soil and the changing needs of the plant. For example, a tree may have a deep, extensive root system that grows over time to support the increasing size and weight of the tree. Other plants, such as annuals, may have shallower and less extensive root systems that grow for only one season before the plant dies.
The rate of root growth can vary depending on many factors, including the type of plant, the age of the plant, and the availability of water and nutrients in the soil. Generally, roots grow faster in warm, moist conditions and more slowly in cold, dry conditions. Some plants, such as the root vegetables carrots and turnips, are specifically grown for their edible roots, which can be harvested when they reach a certain size.
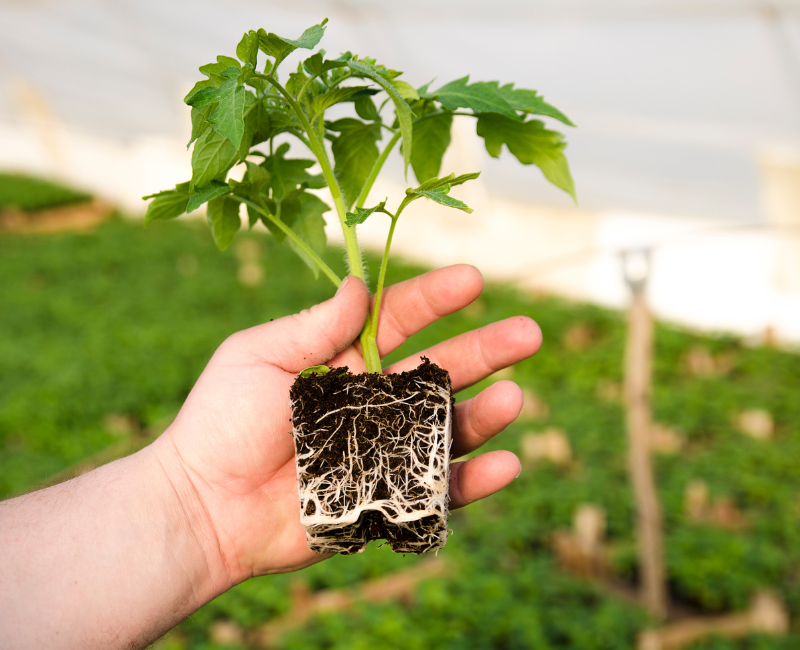

4. Transplantation
Transplanting a plant can be a delicate process, especially if you want to focus on the roots. Here are some general guidelines for transplanting plants and focusing on the roots:
- Water the plant heavily a few days before transplanting to make it easier to remove from the current pot.
- Carefully remove the plant from the pot, taking care not to damage the roots. If the plant is particularly large or difficult to remove, you may need to use a knife to loosen the root ball.
- Inspect the roots to see if they are clumped or damaged. If the roots are tightly bound or appear difficult, you may need to carefully loosen them before transplanting.
- Choose a new pot that is slightly larger than the old one, with drainage holes in the bottom. Fill the pot with fresh potting mix.
- Place the plant in the new pot, trying to spread the roots evenly. Add more soil as needed to cover the roots.
- Water the plant well to help establish the soil and encourage root growth.
- Keep the soil moist, but not too wet, and place the plant in a location with the right amount of light and temperature for its needs.
If you follow these steps, you can carefully transplant your plant and give it the best growing conditions in the new pot.
5. Important things to maintain healthy roots
Here are some tips for keeping your plants' roots healthy:
- Use the right soil: Choose a soil mix that is well-draining and suitable for the type of plant you are growing. Soil that is too wet or poorly draining can cause root rot, while soil that is too dry or nutrient poor can limit root growth.
- Water regularly: Water your plant regularly, but avoid overwatering. Too much water can cause the roots to rot, while not enough water can stress the plant and dry out the roots.
- Provide adequate drainage: Make sure your plant's pot has drainage holes to allow excess water to drain away from the roots. Water retention around the roots can lead to rot.
- Fertilize as needed: Use a balanced fertilizer to provide the plant with the nutrients it needs for growth and health.
- Trim the roots as needed: If your plant's roots become too tightly bound, you may need to trim them to allow the plant to continue growing properly. Use sharp garden shears and be careful not to damage the roots of your plant.
- Provide additional nutrients: This ensures that your plant has access to all the essential nutrients in the right amounts.
6. What happens when the roots are not healthy?
If the roots of the plant are not healthy, it can affect the overall health of the plant. Some possible consequences of unhealthy roots include:
- Slow growth: Unhealthy roots may not be able to absorb the water and nutrients the plant needs to grow. As a result, the plant may grow more slowly or stop growing altogether.
- Poor flowering or fruiting: Plants that have problems with unhealthy roots may also have poor flowering or fruiting. This is because the plant does not have the energy or resources it needs to produce flowers or fruit.
- Increased vulnerability to pests and diseases: Unhealthy plants may be more vulnerable to pests and diseases because their immune systems may be weakened.
- Plant death: In severe cases, unhealthy roots can lead to plant death. This can be the result of a lack of water and nutrients or root rot.
Take good care of your plant's roots to ensure its health and vitality.
7. How to prevent unhealthy roots?
One way to prevent unhealthy roots is to provide the right amount of water for your plant. Here is a story that illustrates this principle:
You adored your new houseplant, a beautiful ficus that you placed in a sunny corner of the room. Water it weekly, making sure the soil is always moist. However, after a few weeks, you notice that the leaves of the ficus begin to turn yellow and fall off.
You're not sure what's going on, so you do a little research and discover that ficuses prefer well-draining soil and should only be watered when the topsoil is dry. Now you know that the plant was overwatered and the excess water was causing the roots to rot.
How to deal with the problem? Remove the plant from the pot and trim any diseased or damaged roots. Then transplant the plant into fresh, well-drained soil and water only when the topsoil is dry. Within a few weeks, the ficus leaves will begin to regain their healthy, green color, and the plant will thrive.
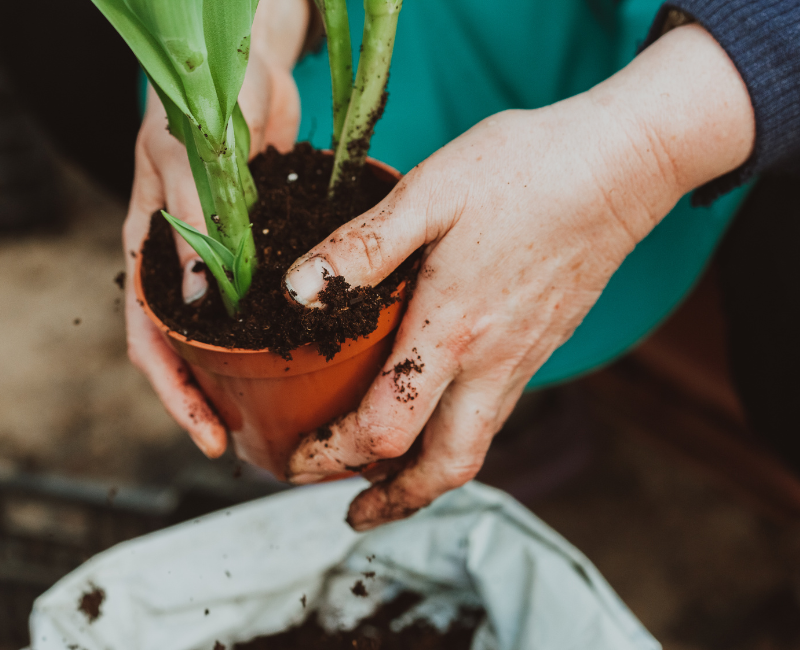

8. How to check the root system of your plant?
- Carefully remove the plant from the pot: One way to check the root system of your plant is to carefully remove it from the pot. Be careful and try not to disturb the roots too much. After removing the plant from the pot, you can inspect the roots to see if they are healthy and growing properly.
- Check for root growth through the drainage holes: If you don't want to disturb the plant by removing it from the pot, you can check for root growth by looking through the drainage holes in the bottom of the pot. This can give you a good idea of the overall health and size of the root system.
- Use a transparent pot: Another option is to use a transparent pot when planting your plant. This will allow you to see the roots as they grow without disturbing the plant by removing it from the pot.
By using one of these methods, you can get a good idea of the health and growth of your plant's root system. This can help you determine if the plant is getting the water and nutrients it needs and if it's time to transplant to a larger pot.
9. Additional tips and tricks
10 additional tips for caring for your plant's roots:
- Choose the right pot size: It is important to use a pot that is the right size for your plant. Too small a pot can lead to overcrowded roots, while too large a pot can lead to excess water and soil that stays too wet, which can lead to root rot.
- Avoid over-fertilizing: While it is important to provide the plant with the nutrients it needs to grow, over-fertilizing can cause excessive leaf growth at the expense of root growth.
- Use a soil mix specifically formulated for the type of plant you are growing: Different plants have different soil requirements. Using a soil mix that is specifically formulated for the type of plant you are growing can help ensure that the plant's roots have access to the proper nutrients and moisture.
- Don't let the plant sit in standing water: Be sure to drain any excess water from the pot after watering, as allowing the plant to sit in standing water can cause root rot.
- Avoid planting too deep: When planting your plant, make sure you follow the recommended planting depth and avoid planting too deep. If the plant is planted too deep, this can lead to a reduced root system and reduced plant growth.
- Provide adequate light: Adequate light is important for plant growth, including root growth. Make sure your plant is getting the right amount of light for its needs.
- Don't let the plant dry out: Allowing your plant to dry out can stress the plant and damage the roots. Be sure to water the plant regularly, but avoid overwatering.
- Avoid using pesticides near the roots: Pesticides can be harmful to the plant's roots, so use sparingly and avoid applying near the plant.
- Don't let the plant become too root bound: If your plant's roots have become too tightly bound and tangled in the pot, this can make it difficult for the plant to absorb water and nutrients. Repot the plant into a larger pot to give the roots room to develop.
- Use Mulch: Mulching around your plant can help conserve soil moisture and keep the roots cool, which can be beneficial for plant growth. Be sure to keep the mulch a few inches away from the base of the plant to prevent excess moisture from building up around the roots.














































































Post comment